(Applies to all e-mails)
The surface meta data shows the e-mail address/name of the originator of the e-mail IE 'From'. It also shows the receivers e-mail address/name IE 'To'
(May apply to some e-mails - depending on the information entered by sender)
Depending on the person sending the e-mail, it may also show other information such as the 'subject' of the e-mail, 'attachments' included, 'cc' information and file size. The body of the e-mail shows the content, from which a person can determine what the e-mail is about and who it's intended for.
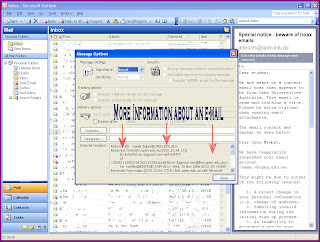
I can find out more information by 'right clicking' on an email and choosing the 'options' tag from the drop down list. This gives me access to other information such as the 'IP' address of the e-mail, the path the e-mail took to get to me, the time it was sent and other valuable information. (see pic below)
2. In what cases would you find it useful to use the 'cc', 'bcc' and 'reply all functions of email?
'CC' - Carbon Copy - When you want all parties to to see who the other recipients of the e-mail are. This is a non-preferred way of sending e-mails as it give all recipients access to every ones e-mail address.
'BCC' - Blind Carbon Copy or Blind Courtesy Copy - A great way to send to multiple recipients yet making it personal. The recipients will have the impression that you wrote your e-mail just for them. Also protects the e-mails recipients fro getting spam mail as their e-mail address is hidden from all others on the 'bcc' list.
'Reply' - Request for a response - The e-mail sender may request for a reply to ensure that the receiver has got the e-mail to act or respond to it. The receiver may choose to reply to an e-mail on their own, especially if the e-mail sender is asking questions in the body of the e-mail and is expecting an answer.
3. In what ways can you ensure that an attachment you send will be easily opened by the receiver?
Make the attachments small in byte size so that the e-mail receiver can download it easily and quickly - especially if they are pictures.
The e-mail can also be sent in an ASCII form, which is a code form that does not include special formatting features and can be read by most computers. (see links below for more info)'CC' - Carbon Copy - When you want all parties to to see who the other recipients of the e-mail are. This is a non-preferred way of sending e-mails as it give all recipients access to every ones e-mail address.
'BCC' - Blind Carbon Copy or Blind Courtesy Copy - A great way to send to multiple recipients yet making it personal. The recipients will have the impression that you wrote your e-mail just for them. Also protects the e-mails recipients fro getting spam mail as their e-mail address is hidden from all others on the 'bcc' list.
'Reply' - Request for a response - The e-mail sender may request for a reply to ensure that the receiver has got the e-mail to act or respond to it. The receiver may choose to reply to an e-mail on their own, especially if the e-mail sender is asking questions in the body of the e-mail and is expecting an answer.
3. In what ways can you ensure that an attachment you send will be easily opened by the receiver?
Make the attachments small in byte size so that the e-mail receiver can download it easily and quickly - especially if they are pictures.
4. What sorts of filters or rules do you have set up, and for what purpose?
My e-mail software (Microsoft Office Outlook) has been configured and set up to filter spam mail. However, I have to create rules almost every time I check my e-mails as there are spam e-mails that come through almost all the time.
When I create rules, it blocks e-mails from the senders and sends them to the 'junk' e-mail folder to be deleted automatically.
The purpose of setting up the filters and rules is to weed out e-mails that are just plain useless to me!
My e-mail software (Microsoft Office Outlook) has been configured and set up to filter spam mail. However, I have to create rules almost every time I check my e-mails as there are spam e-mails that come through almost all the time.
When I create rules, it blocks e-mails from the senders and sends them to the 'junk' e-mail folder to be deleted automatically.
The purpose of setting up the filters and rules is to weed out e-mails that are just plain useless to me!
5. How have you organised the folder structure of your email and why?
My e-mail folders are structured as follows:
- deleted items
- drafts
- inbox
- junk e-mail
- outbox
- sent items
- search folders
When I open my e-mail programme, it opens up in my 'inbox' folder. The list of e-mails are sorted out in date order, the latest e-mail being first on the list.
The reason why I've set it up this way is to ensure that I read and act upon every e-mail that I receive.
The reason why I've set it up this way is to ensure that I read and act upon every e-mail that I receive.

No comments:
Post a Comment